Previous Year Paper(Oct 2022)
Total = 60 marks
(8 + 20 + 32)
Section A(2m x 4q = 8)
Q1. Define Database and Database Management system.
A database is a structured collection of data that is stored and accessed in a computer system
- Databases are used to organize and manage related data, such as company information, banking transactions, and customer details.
A database management system (DBMS) is a software tool that allows users to create, manage, and manipulate databases:
- Store data: DBMSs help organizations store and organize large amounts of data.
- Retrieve data: DBMSs help users find and access information quickly and easily.
- Secure data: DBMSs keep data safe from unauthorized people and ensure only those with valid permissions can access it.
- Maintain data integrity: DBMSs ensure that data is consistently organized and remains easily accessible.
Q2. What is data model? Name three categories of data model.
Data models are conceptual representations of how data is organized and structured.
- They provide a blueprint for storing, managing, and retrieving data in a database or data storage system.
- There are several types of data models, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Here are some:
- Relational Data Model
- Hierarchical Data Model
- Network Data Model
Q3. What is key attribute? Give an example.
A key attribute is a property that uniquely identifies an entity and is mapped to the primary key field in a database.
- In an ER diagram, you would draw an oval with underlined text
- Example: Student_ID in a table called STUDENT
Q4. List data types allowed in SQL.
Common Datatypes in SQL are:
- INTEGER
- VARCHAR(n)
- DATE
- BOOLEAN
- JSON
Q5. What is transaction control language? List any two transaction control commands.
In the database, Transaction Control Language (TCL) commands are used to govern transactions.
- This command is used to manage changes to DML statements.
- TCL allows you to create logical transactions by combining your statements.
Types:
Commit Command:
- This command is used to save all the transactions in the DB.
- Syntax:
COMMIT; - For Example,
- SQL
UPDATE Student SET DOB=’2005-03-27’ WHERE Stu_Name=’Joey’;` COMMIT; - Thus, this example would insert the DOB in the given table, which has the name = Joey and then COMMIT these changes in the DB.
ROLLBACK Command:
- The “rollback” term refers to the method of undoing changes.
- Thus, this command could only be used in order to reverse transactions that occurred since the last ROLLBACK or COMMIT command.
- All the modifications must be cancelled in case any SQL grouped statements produce a certain error.
- Syntax:
ROLLBACK; - For Example:
- SQL
UPDATE Student SET DOB=’2005-03-27’ WHERE Stu_Name=’Joe’; ROLLBACK;
- The example given above would insert the DOB in a table that has name = Joey and then ROLLBACK these changes in the DB.
- Thus, this type of operation would not create an impact on the table.
- The “rollback” term refers to the method of undoing changes.
Q6. What is concurrency control?
Concurrency Control is the process of ensuring simultaneous execution or updation of data by several processes or users
- This is done while maintaining data consistency and integrity
Section B(5m x 4q = 20)
Q7. Explain the main characteristics of Database approach.
Q8. What is data independence? Explain briefly about the types of data independence.
Data independence is a property of a database management system by which we can change the database schema at one level of the database system without changing the database schema at the next higher level.
It has two types:
- Logical Independence: Changes in the logical structure don't affect user applications.
- Physical Independence: Changes in physical storage don't affect the logical structure.
Q9. What is an ER diagram? Explain different notations used in drawing ER diagram.
The Entity Relationship Diagram explains the relationship among the entities present in the database.
- ER models are used to model real-world objects like a person, a car, or a company and the relation between these real-world objects

- Rectangles illustrate the entity set.
- A Strong Entity Set only has a single border.
- It is defined by its own set of attributes
- A Weak Entity Set has two borders
- It is always associated with another Entity Set(which is called the Identifier Entity Set)
- A Strong Entity Set only has a single border.
- Diamond illustrates the relationship between the entity set.
- A Strong Relationship has a single border
- Here, the Child Entity is completely dependent on the Parent Entity.
- A Weak Relationship has two borders
- A weak Relationship is where a child Entity can exist without the Parent Entity.
- A Strong Relationship has a single border
- Ellipse illustrates the attributes of an entity set.
- A simple Attribute has a single outer border
- It cannot be further divided into sub-parts. Example, id attribute
- It is also known as a Single-Valued Attribute
- A Multi-Valued Attribute has 2 outer borders
- This means it has more than one value for a given entity.
- Eg. phone_number may have multiple numbers stored
- This means it has more than one value for a given entity.
- A Composite Attribute has subparts derived from it.
- It can be broken down into subparts. Example, name can be broken down into first_name and last_name
- A Derived Attribute has a dotted border
- It means the data in this attribute was derived from another attribute
- For Example, age was Derived from date_of_birth
- It means the data in this attribute was derived from another attribute
- A simple Attribute has a single outer border
- Lines illustrate the association of attributes to the entity set and the association of entity set to the relationship set.
Q10. Create an employee table using the following fields.
| Field name | Data type |
|---|---|
| EMPNO | NUMBER |
| ENAME | CHAR |
| DOB | Date |
| Dept | String |
| Salary | Real |
- Create the Table.
- Insert 5 tuples.
- Find the sum of salaries.
- Find department wise count of Employees
- Display the tuples in the order of average salaries of Employees.
Ans.
Create the Table:
CREATE TABLE Employee(EMPNO NUMBER Primary Key, ENAME VARCHAR(100), DOB Date, DEPT VARCHAR(100), SALARY Real);Insert Data:
INSERT INTO Employee VALUES(101, 'Souhrud', TO_DATE('27-06-2005', 'DD-MM-YYYY'),'Electronics', 32000);
INSERT INTO Employee VALUES(102, 'Nanda', TO_DATE('6-11-2004', 'DD-MM-YYYY'), 'Design', 34000);
INSERT INTO Employee VALUES(103, 'Joel', TO_DATE('30-06-2005', 'DD-MM-YYYY'), 'Software', 29500);
INSERT INTO Employee VALUES(104, 'Nikhil', TO_DATE('6-01-2005', 'DD-MM-YYYY'), 'Hardware', 30000);
INSERT INTO Employee VALUES(105, 'Varun', TO_DATE('16-03-2005', 'DD-MM-YYYY'), 'Software', 29000);Display Once to Verify:
SELECT * FROM Employee;| EMPNO | ENAME | DOB | DEPT | SALARY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | Souhrud | 27-JUN-05 | Electronics | 32000 |
| 102 | Nanda | 06-NOV-04 | Design | 34000 |
| 103 | Joel | 30-JUN-05 | Software | 29500 |
| 104 | Nikhil | 06-JAN-05 | Hardware | 30000 |
| 105 | Varun | 16-MAR-05 | Software | 29000 |
Show Sum Of Salary:
SELECT SUM(SALARY) As TOTAL_SALARY FROM Employee;| TOTAL_SALARY |
|---|
| 154500 |
Department Count:
SELECT DEPT, COUNT(*) As Employee_Count
FROM Employee
GROUP BY DEPT;| DEPT | EMPLOYEE_COUNT |
|---|---|
| Electronics | 1 |
| Software | 2 |
| Design | 1 |
| Hardware | 1 |
Order by Average:
SELECT DEPT, AVG(SALARY) As Avg_Salary
FROM Employee
GROUP BY DEPT
ORDER BY Avg_Salary;| DEPT | AVG_SALARY |
|---|---|
| Software | 29250 |
| Hardware | 30000 |
| Electronics | 32000 |
| Design | 34000 |
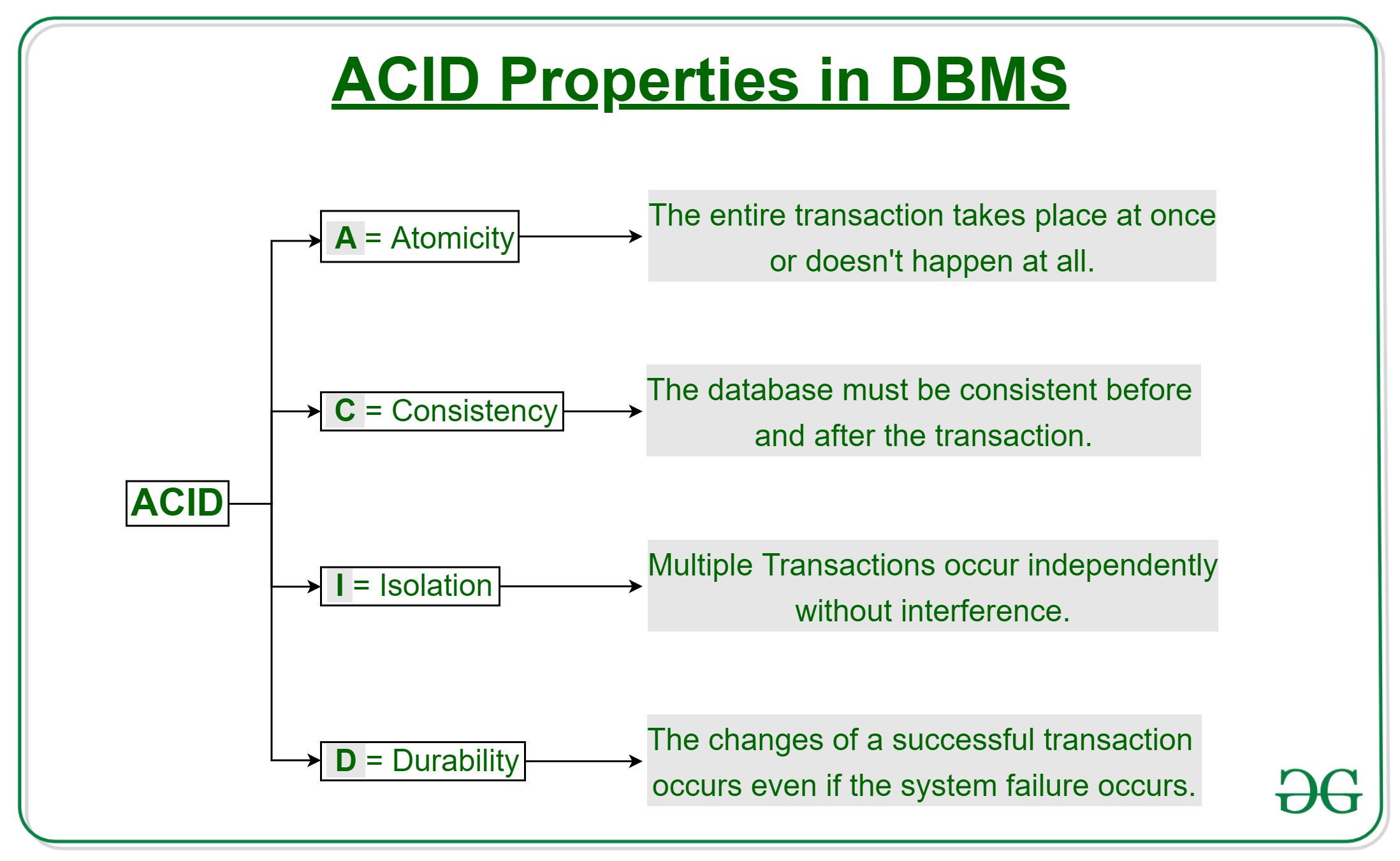
Q11. What is a transaction? Explain ACID properties of a transaction.
A transaction is a single logical unit of work that accesses and possibly modifies the contents of a database.
- Transactions access data using read-and-write operations.
- To maintain consistency in a database, before and after the transaction, certain properties are followed.
- These are called ACID properties.
The acronym ACID stands for Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. ACID Can be broken down to:
- Atomicity:
- By this, we mean that either the entire transaction takes place at once or doesn’t happen at all. There is no midway i.e. transactions do not occur partially.
- Each transaction is considered as one unit and either runs to completion or is not executed at all
- It involves the following two operations.
- Abort : If a transaction aborts, changes made to the database are not visible.
- Commit : If a transaction commits, changes made are visible.
- Atomicity is also known as the ‘All or nothing rule’.
- Consistency:
- This means that integrity constraints must be maintained so that the database is consistent before and after the transaction.
- It refers to the correctness of a database.
- Isolation:
- This property ensures that multiple transactions can occur concurrently without leading to the inconsistency of the database state.
- Transactions occur independently without interference.
- Changes occurring in a particular transaction will not be visible to any other transaction until that particular change in that transaction is written to memory or has been committed.
- Durability:
- This property ensures that once the transaction has completed execution, the updates and modifications to the database are stored in and written to disk and they persist even if a system failure occurs.
- These updates now become permanent and are stored in non-volatile memory.
- The effects of the transaction, thus, are never lost.
Q12. Write a short note on database backup and database recovery.
Database Backup and Recovery
Database backup and recovery are critical components of database management that ensure data integrity and availability in the event of data loss, corruption, or system failure.
Database Backup: A database backup is a copy of the database that can be used to restore the original after a data loss event. Backups can be full, incremental, or differential:
- Full Backup: A complete copy of the entire database at a specific point in time.
- Incremental Backup: A backup that captures only the changes made since the last backup, whether it was full or incremental.
- Differential Backup: A backup that captures all changes made since the last full backup.
Backups can be stored on various media, including local disks, external drives, or cloud storage. Regular backups are essential to protect against data loss due to hardware failures, accidental deletions, or disasters.
Database Recovery: Database recovery is the process of restoring a database from a backup to bring it back to a consistent state after a failure. Recovery strategies can vary based on the type of failure:
- Crash Recovery: Automatically restores the database to a consistent state after a system crash using transaction logs.
- Media Recovery: Involves restoring the database from backups when data is lost due to hardware failure or corruption.
- Point-in-Time Recovery: Allows the database to be restored to a specific moment, useful for recovering from accidental data modifications.
Recovery procedures must be well-documented and tested to ensure that they can be executed quickly and effectively when needed.
Section C(8m x 4q = 32)
Q13. Explain three schema architecture with a neat diagram.
The three schema architecture is also called ANSI/SPARC architecture or three-level architecture.
- This framework is used to describe the structure of a specific database system.
- The three schema architecture is also used to separate the user applications and physical database.
- The three schema architecture contains three-levels. It breaks the database down into three different categories.
 In the above diagram:
In the above diagram:
- It shows the DBMS architecture.
- Mapping is used to transform the request and response between various database levels of architecture.
- Mapping is not good for small DBMS because it takes more time.
- In External / Conceptual mapping, it is necessary to transform the request from external level to conceptual schema.
- In Conceptual / Internal mapping, DBMS transform the request from the conceptual to internal level.
Q14. Discuss the different types of indexes.
Indexing enhances database performance by reducing the number of disk visits needed to execute a query. It is a data structure technique that uses key fields to create indexes, with the main or candidate key appearing as the Search key in the first column, often sorted for faster retrieval. While sorting is not mandatory, it aids in efficiency. The second column, known as the Data Reference or Pointer, contains pointers to the disk block addresses where the corresponding key values are stored.
- Primary Indexing Primary indexing is applied to the primary key of a table, ensuring that data can be accessed quickly without scanning the entire table.
- Secondary Indexing Secondary indexing provides an additional access path to data stored in a table, allowing for efficient searches based on non-primary key columns.
- Clustered Index: A clustered index determines the physical order of data in a table. When a clustered index is created, the rows are sorted and stored according to the values of the indexed column(s).
Q15. Draw an ER diagram for Bank Database with 5 entities and 5 attributes for each entity. Specify the cardinality ratio on each of the relationships existing between entities.
TODO: Solve
Q16. Explain different relational algebra operations.
Relational algebra is a procedural query language, which takes instances of relations as input and yields instances of relations as output. It uses operators to perform queries.
An operator can be either unary or binary. They accept relations as their input and yield relations as their output.
Types:
Unary
- The operations that operate on only one relation are called unary operations in relational algebra. The three unary operations in relational algebra are:
- Selection
- The selection operation is a unary operation that is performed on one relation.
- The selection operation is used to retrieve tuples from the relation that satisfies the given condition.
- It is denoted by σ (sigma)
- Projection
- Project operation selects (or chooses) certain attributes discarding other attributes.
- The Project operation is also known as vertical partitioning since it partitions the relation or table vertically discarding other columns or attributes.
- It is denoted by π (pi)
- Rename
- The rename operation is operation applied on one relation.
- Rename operation (as the name suggests) is used to rename the relation, attributes or both.
- It is denoted by ρ (rho)
- Selection
- The operations that operate on only one relation are called unary operations in relational algebra. The three unary operations in relational algebra are:
Binary
- The operations that operate on two relations are called binary operations in relational algebra. The three binary operations in relational algebra are:
- Union
- It performs binary union between two given relations
- It is denoted by ∪ (union)
- Set Difference
- The result of set difference operation is tuples, which are present in one relation but are not in the second relation.
- It is denoted by − (Minus Symbol)
- Cartesian Product
- Combines information of two different relations into one.
- It is denoted by X (Multiplication X)
- Union
- The operations that operate on two relations are called binary operations in relational algebra. The three binary operations in relational algebra are:
Q17. What is Normalization? Differentiate between 3NF and BCNF.
BCNF Normalization is the process of minimizing redundancy from a relation or set of relations.
- Redundancy in relation may cause insertion, deletion, and update anomalies.
- So, it helps to minimize the redundancy in relations.
- Normal forms are used to eliminate or reduce redundancy in database tables.
- What normalization basically does is ensure that your data is free of data redundancy or duplicate data and does not have data anomalies that would otherwise compromise its integrity.
Levels of Normalization:
- First Normal Form (1NF)
- Second Normal Form (2NF)
- Third Normal Form (3NF)
- Boyce-Codd Normal Form (BCNF)
Explanation:
- Third Normal Form (3NF):
- 3NF builds on 2NF by requiring that all non-key attributes are independent of each other.
- This means that each column should be directly related to the primary key, and not to any other columns in the same table.
- Boyce-Codd Normal Form (BCNF):
- BCNF is a stricter form of 3NF that ensures that each determinant in a table is a candidate key.
- In other words, BCNF ensures that each non-key attribute is dependent only on the candidate key.
(GeeksForGeeks, Explanation)(GeeksForGeeks, Forms)
Q18. Explain different states of a transaction with a neat diagram.
Transaction in DBMS is a set of logically related operations executed as a single unit.
- These logic are followed to perform modification on data while maintaining integrity and consistency
- Example: Adding student1's exam result to the database
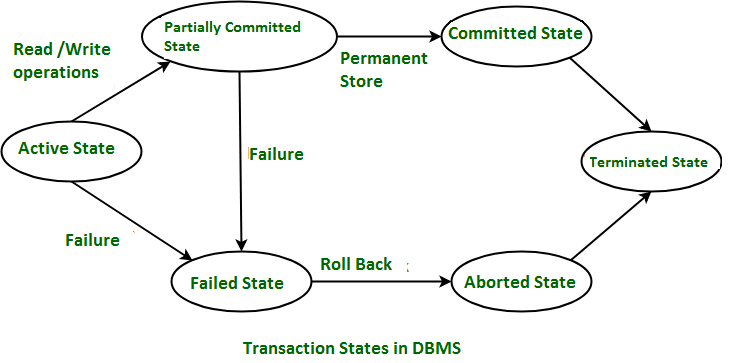
- These are different types of Transaction States :
- Active State
- When the instructions of the transaction are running then the transaction is in active state. If all the ‘read and write’ operations are performed without any error then it goes to the “partially committed state”; if any instruction fails, it goes to the “failed state”.
- Partially Committed
- After completion of all the read and write operation the changes are made in main memory or local buffer. If the changes are made permanent on the DataBase then the state will change to “committed state” and in case of failure it will go to the “failed state”.
- Failed State
- When any instruction of the transaction fails, it goes to the “failed state” or if failure occurs in making a permanent change of data on Database.
- Aborted State
- After having any type of failure the transaction goes from “failed state” to “aborted state” and since in previous states, the changes are only made to local buffer or main memory
- Hence these changes are deleted or rolled-back.
- Committed State
- It is the state when the changes are made permanent on the Data Base and the transaction is complete and therefore terminated in the “terminated state”.
- Terminated State
- If there isn’t any roll-back or the transaction comes from the “committed state”, then the system is consistent and ready for new transaction and the old transaction is terminated.
- Active State