PYQs(July 2024)
Section A
(5 x 2M = 10)
Question 1a. Who is a leader?
A person who possesses attributes of leadership is known as a leader. A leader may or may not be formally appointed or elected. He can be a successful leader if people accept him wholeheartedly. For example, Mahatma Gandhi was successful in leading people without occupying a formal position.
Question 1b. State any two qualities of a good leader.
The two qualities of a good leader are:
- Communicating.
- Motivating
Question 1c. Give the meaning of transactional leadership.
Transactional leader brings followers together on a joint purpose of the goal. They are the managerial leaders who supervise and organize the followers in such a way that the performance of the team is not affected and the goal is achieved, for every achievement there are some reward and punishment on the failure.
Question 1d. What do you mean by emotional management?
Emotional management is a set of skills that can help you react constructively to people or events. Learning how to manage your emotions can benefit your career by helping you make rational choices and develop relationships with others.
Question 1e. Give the meaning of autocratic leadership.
An authoritarian leadership style is described as being as "leaders' behavior that asserts absolute authority and control over subordinates and [that] demands unquestionable obedience from subordinates."
- Such a leader has full control of the team, leaving low autonomy within the group.
Question 1f. Give the meaning of leadership values.
Leadership values are the core beliefs and principles that guide leaders and managers in their personal and professional lives and allow them to oversee, lead and manage others effectively.
- Your values are the things you believe are most important to achieving your goals and being happy.
Question 1g. Define informal leadership.
Informal leadership refers to the influence someone has on others within an organization without holding a formal leadership position.
- These leaders gain respect and trust through their expertise, relationships, and positive influence, rather than through a title or hierarchical power
- Influence without Authority
- Because of built/accumulated trust, relationships and respect
Section B
(3 x 4M = 12)
Question 2. Briefly explain the functions of leadership.
The functions of leadership are as follows:
1. Setting Vision and Goals:
- Leaders define a clear vision and specific goals, providing direction and purpose for the team.
2. Motivating and Inspiring:
- They inspire and motivate team members, celebrating achievements to foster a positive work environment.
3. Communicating:
- Effective leaders ensure clear communication and smooth information flow within the team.
4. Decision-Making:
- Leaders make informed decisions in complex situations by analyzing information and considering various perspectives.
5. Developing Others:
- They invest in team members' growth through coaching, mentoring, and skill enhancement opportunities.
6. Building Relationships:
- Leaders cultivate strong, trusting relationships and promote collaboration while resolving conflicts constructively.
7. Managing Resources:
- They efficiently allocate resources—time, budget, and personnel—to achieve optimal results.
8. Problem-Solving:
- Leaders identify challenges and use critical thinking and creativity to find solutions.
9. Creating a Positive Culture:
- They shape organizational culture by promoting values like integrity and inclusivity, leading by example.
10. Monitoring and Evaluating:
- Leaders continuously assess progress and outcomes, using feedback to improve performance.
Question 3. Explain the traits of an ethical leader.
The traits of an ethical leader are as follows:
1. Lead by Example:
- Ethical leaders model ethical behavior, motivating followers to act similarly and assisting them in their daily tasks for better understanding.
2. Adaptability to Change:
- They quickly adapt to changing circumstances, guiding the organization through transitions as it evolves.
3. Treating Everyone Equally:
- Ethical leaders respect all team members equally, fostering a fair and harmonious workplace atmosphere.
4. Open Communication:
- They excel in communication, promoting transparency and trust within the organization, allowing for free exchange of ideas.
5. Effective Stress Management:
- Ethical leaders manage their own stress and help followers cope with stress, creating a calm and supportive work environment.
6. Good Mediator:
- They effectively mediate conflicts, listening to all sides and finding fair solutions that satisfy both parties.
Question 4. State any four differences between manager and leader.
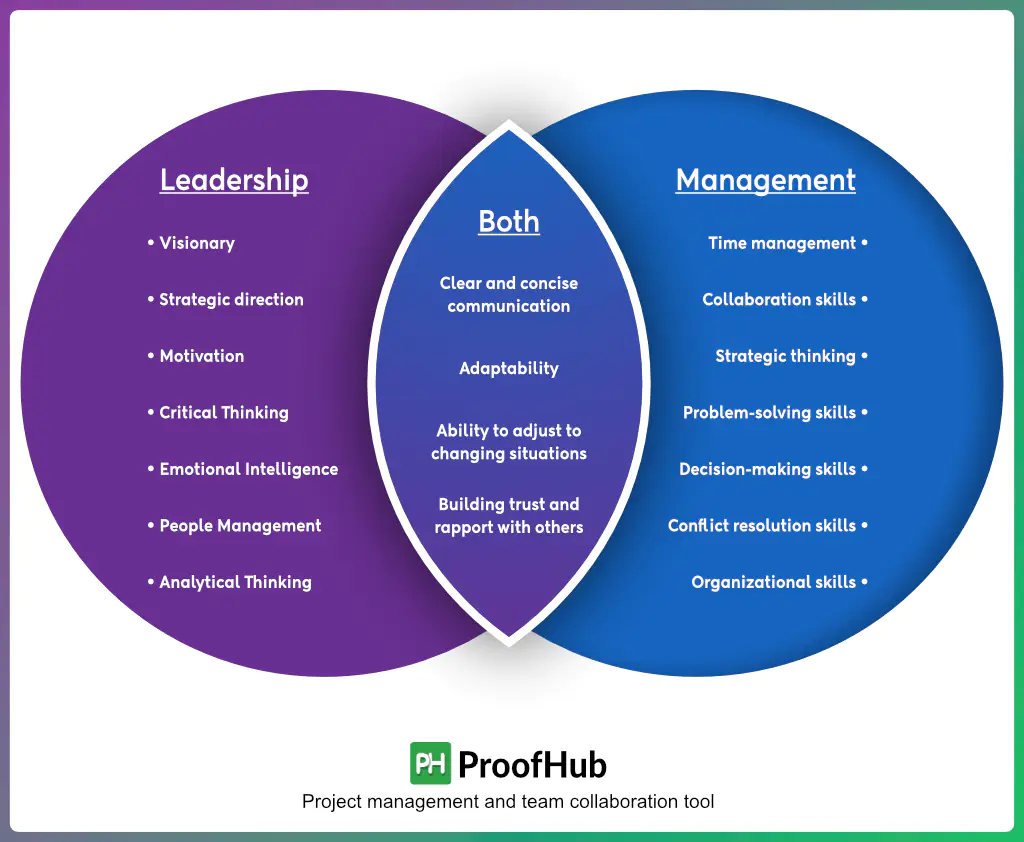
| Basis of Difference | Leadership | Management |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Primary Focus | Leaders focus on the "what" and "why," establishing a vision and direction for the future | Managers concentrate on the "how" and "when," focusing on executing plans to achieve the set vision |
| 2. Core Function | The function of a leader is to inspire, motivate, and guide people toward a shared goal, often with an emphasis on innovation and change | A manager's function is to plan, organize, and oversee processes to achieve specific objectives by maintaining control and stability |
| 3. Approach | Leadership relies on personal influence, trust, and respect to encourage people to work towards a common objective | Management uses the formal authority granted by their position to direct and control others to complete tasks |
| 4. Perspective on Change | A leader embraces chaos and sees change as an opportunity to adapt and evolve the organization's vision | A manager seeks a stable environment and controls various factors to ensure that articulated goals are accomplished efficiently |
| 5. Role Definition | The role of a leader is fluid and not confined to a title; it's about creating a vision and inspiring people through action | A manager's role is formally defined with a specific job description and a fixed set of responsibilities within the organization |
| 6. Key Skills | Essential skills include vision, emotional intelligence, adaptability, and inspiring communication to motivate people | Key skills include organization, delegation, time management, and conflict resolution to handle day-to-day operations effectively |
Question 5. Describe the importance of communication skills in leadership.
When it comes to business, clear and effective communication from leadership offers a multitude of benefits to employers and employees:
- One such benefit is that it keeps employees aware of individual and organizational goals.
- When workers understand what is expected of them, they are more likely to be able to deliver the desired results, which can help increase job satisfaction, improve morale, and boost confidence.
- Successful leaders must be able to inspire their employees.
- If leaders are not strong communicators, it will negatively affect the motivation and, consequently, the productivity of their teams.
- Conversely, when objectives and expectations are well-defined—and teams are collaborating to meet them—it can promote efficiency, enhance engagement, and improve overall work performance.
- Strong leadership communication helps ensure that team members are aware of organizational challenges and opportunities
- This enables them to make more informed decisions that ultimately benefit the bottom line
Question 6. Explain any four characteristics of Laissez-faire leadership.
Let go. Let it be. This is what the term laissez-faire means when translated. Laissez-faire is often used to describe an laissez-faire economics or political policy, but is also used regularly in the business world to describe a leadership style.
Laissez-faire leaders have an attitude of trust and reliance on their employees. They don’t micromanage or get too involved, they don’t give too much instruction or guidance.
- Instead laissez-faire leaders let their employees use their creativity, resources, and experience to help them meet their goals.
- This kind of leadership is very hands-off—managers trust their employees and are confident in their abilities.
- They give guidance and take responsibility where needed, but this leadership style means that subordinates and team members have the real lead.
There are many common characteristics of the laissez-faire leadership style including:
- Little guidance from leaders
- Employees have the ability to make decisions
- People are expected to solve their own problems
- Access to many resources and tools
- Constructive criticism from leaders
- Leaders take charge when necessary
- Leaders take responsibility for overall actions and decisions
These leadership characteristics may also be found in other leadership styles, and many elements of leadership are fluid and work across management styles.
Section C
(3 x 10M = 30)
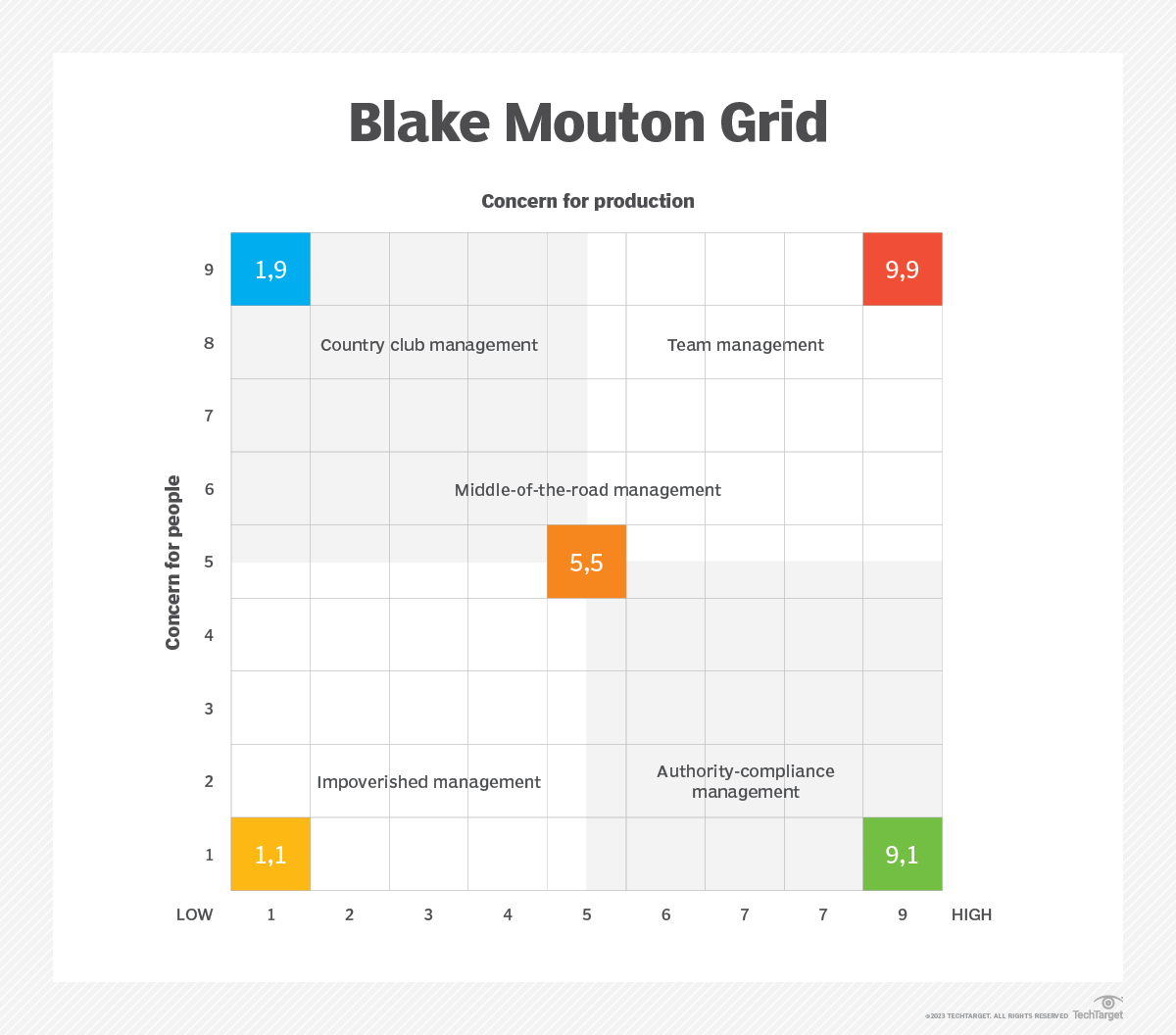
Question 7. Explain Blake and Mouton's managerial grid theory of leadership.
The managerial grid model(The Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid model) is a self-assessment tool by which individuals and organizations can identify a manager's or leader's style.
- The grid was originally developed by Robert R. Blake and Jane S. Mouton in the 1960s and has evolved in subsequent decades.
The Blake Mouton Grid is created using a horizontal axis and a vertical axis that meet at a right angle and are rated on a nine-point scale:
- Horizontal axis -- concern for production.
- A one, or low concern for production, is placed to the far left of the horizontal axis, close to the right angle; a nine, or high concern for production, is located on the far right of the horizontal line.
- A high concern for production indicates that the leader prioritizes objectives, results and productivity when determining how a task should be accomplished.
- Vertical axis -- concern for people.
- A one, or low concern, falls at the bottom of the vertical line, close to the base near the right angle, while a nine, or high concern for people, is placed at the top of this vertical axis.
- A high concern for people indicates that the leader prioritizes the needs and interests of people when determining how a task should be accomplished.
Question 8. Elaborate the different roles of leadership.
The different roles of leadership are:
1. Coach:
- Leaders act as coaches, providing support and feedback to help employees succeed in their roles. They create opportunities for team members to showcase their skills and offer constructive criticism through individual meetings.
2. Networker:
- Effective leaders build connections both within and outside the organization. By attending seminars and corporate events, they strengthen relationships with colleagues, suppliers, and customers, facilitating business growth.
3. Communicator:
- Good communication is essential for leaders. They must convey information clearly to team members, clients, and suppliers, sharing meeting details, strategies, and goals in a motivating manner. This includes both verbal and written communication skills.
4. Delegator:
- Leaders delegate tasks based on team members' strengths and weaknesses. This not only helps in achieving organizational goals but also provides employees with opportunities to learn new skills and demonstrate their capabilities.
5. Strategist:
- As strategists, leaders develop overarching goals and processes to achieve success. They share their vision with the team, guiding them toward common objectives and becoming a sought-after source of guidance.
6. Role Model:
- Leaders serve as role models, inspiring team members through their values and actions. By encouraging and mentoring their teams, they foster a culture of hard work and responsibility.
7. Motivator:
- Leaders motivate their team members to reach their potential. By inspiring employees, they create an environment where individuals are encouraged to work hard and take on greater responsibilities.
8. Adopter:
- Adaptability is crucial for leaders. They must be flexible and ready to face uncertainties, quickly adjusting to changes such as budget cuts or shifts in project plans without losing morale.
9. Trainer:
- Leaders play a vital role in training employees, helping them acquire new skills and understand new procedures. This fosters a culture of continuous learning and productivity.
10. Innovator:
- As innovators, leaders seek to introduce new processes and encourage creativity within the team. They understand that innovation is essential for organizational growth and motivate employees to contribute new ideas.
Question 9. Discuss the significance of communication skills in leadership.
When it comes to business, clear and effective communication from leadership offers a multitude of benefits to employers and employees:
- One such benefit is that it keeps employees aware of individual and organizational goals.
- When workers understand what is expected of them, they are more likely to be able to deliver the desired results, which can help increase job satisfaction, improve morale, and boost confidence.
- Successful leaders must be able to inspire their employees.
- If leaders are not strong communicators, it will negatively affect the motivation and, consequently, the productivity of their teams.
- Conversely, when objectives and expectations are well-defined—and teams are collaborating to meet them—it can promote efficiency, enhance engagement, and improve overall work performance.
- Strong leadership communication helps ensure that team members are aware of organizational challenges and opportunities
- This enables them to make more informed decisions that ultimately benefit the bottom line
Question 10. Explain the competency and behavioural approaches to leadership.
Leadership theories can be broadly categorized into two significant approaches: competency and behavioral approaches. Each offers unique insights into what makes an effective leader.
Competency Approach
- Skill Identification:
- Competencies are often categorized into technical, interpersonal, and conceptual skills. Technical skills involve specific knowledge related to a field, interpersonal skills pertain to communication and relationship-building, and conceptual skills involve the ability to understand complex situations and develop strategic solutions.
- Assessment and Development:
- Organizations often use competency frameworks to assess potential leaders and identify areas for development. This can include performance evaluations, 360-degree feedback, and training programs aimed at enhancing specific competencies.
- Focus on Results:
- The competency approach emphasizes measurable outcomes. Leaders are evaluated based on their ability to achieve organizational goals, drive performance, and foster team success.
- Examples of Competencies:
- Common competencies include decision-making, emotional intelligence, adaptability, and conflict resolution. Leaders who excel in these areas are often more effective in their roles.
Behavioral Approach
- Leadership Styles:
- The behavioral approach categorizes leaders into different styles based on their behaviors. Common styles include autocratic, democratic, and laissez-faire leadership. Each style has distinct characteristics and impacts team dynamics differently.
- Focus on Actions:
- This approach emphasizes what leaders do rather than who they are. It looks at how leaders interact with their teams, make decisions, and communicate. Effective behaviors include providing support, fostering collaboration, and encouraging participation.
- Training and Development:
- The behavioral approach suggests that leadership can be cultivated through training and practice. Organizations can implement programs that focus on developing specific leadership behaviors, such as effective communication and team-building skills.
- Research Foundations:
- Studies such as the Ohio State Leadership Studies and the University of Michigan Studies have identified key behaviors associated with effective leadership, such as consideration (supporting team members) and initiating structure (defining roles and tasks).
Question 11. Discuss in brief about moral leadership.
Moral leadership refers to the practice of leading with a strong ethical foundation, prioritizing values such as integrity, fairness, and social responsibility. It emphasizes the importance of ethical behavior in decision-making and the impact of a leader's actions on their followers and the broader community. Here are some key aspects of moral leadership:
1. Ethical Decision-Making:
- Moral leaders are committed to making decisions that align with ethical principles. They consider the consequences of their actions on all stakeholders, including employees, customers, and the community.
2. Integrity and Authenticity:
- Moral leaders demonstrate integrity by being honest and transparent in their actions. They are authentic, aligning their words with their actions, which builds trust and credibility among their followers.
3. Empowerment and Inclusivity:
- Moral leadership involves empowering others and promoting inclusivity. Moral leaders encourage diverse perspectives and ensure that all voices are heard, fostering a collaborative and respectful environment.
4. Social Responsibility:
- Moral leaders recognize their responsibility to contribute positively to society. They engage in practices that promote sustainability, social justice, and community well-being, often going beyond profit motives.
5. Role Modeling:
- By exemplifying ethical behavior, moral leaders serve as role models for their teams. Their actions inspire others to act ethically and uphold similar values, creating a culture of integrity within the organization.
6. Long-Term Perspective:
- Moral leadership focuses on long-term outcomes rather than short-term gains. Leaders prioritize sustainable practices and ethical considerations, understanding that these contribute to lasting success and reputation.
Section D
(1 x 8M = 8)
Question 12. Compare and contrast formal and informal leadership
| Basis for Comparison | Formal Leadership | Informal Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Source of Authority | Authority is derived from an official position or title within the organization's hierarchy. | Influence stems from the trust, respect, experience, and knowledge recognized by peers, not from a formal title. |
| 2. Role Definition | The role is officially designated with a specific job description and a defined set of responsibilities. | The role is unofficial and not based on a formal position; they are considered leaders by their colleagues due to their actions and qualities. |
| 3. Decision-Making | Decisions are typically made by the leader, sometimes with input from select advisors, but the final authority rests with them. | Decision-making is often collaborative, involving input and agreement from other group members. |
| 4. Method of Influence | Influences others through legitimate power, commands, and the ability to reward or punish. | Influences others through charisma, expertise, open communication, and building strong interpersonal relationships. |
| 5. Scope of Relationships | Relationships are often limited and structured, primarily with direct reports and other leaders within the formal hierarchy. | Relationships are typically broad and span across various departments and levels of the organization. |
| 6. Primary Focus | The primary focus is on achieving the organization's goals, maintaining stability, and adhering to established procedures. | The focus is often on the well-being and interests of colleagues, fostering teamwork, and providing guidance and support. |
| 7. Examples | A CEO, a department manager, or a military officer who has been officially appointed to a position of power. | A knowledgeable colleague whom others seek for advice, or a team member who naturally motivates the group during a project. |
Question 13. Write a short note on:
- Democratic Leadership
- Autocratic Leadership
Democratic Leadership
Democratic leadership, which is also commonly known as participative leadership, is about letting multiple people participate in the decision-making process. This type of leadership can be seen in a wide range of contexts, from businesses to schools to governments.
| Pros | Cons | | Encourages collaoration | The minority opinion is overridden | | Welcoming of a variety of opinions and ways of thinking | The involvement of multiple people can lead to more communication gaps and confusion | | Leads to higher group engagement and productivity | Can take a longer time to come to a decision | | Can result in more creative solutions | An unskilled or untrained group can result in more decision making |b | The outcome is supported by the majority | Near impossible to make everyone happy |
Autocratic Leadership
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795314-what-is-autocratic-leadership-5b114f573037130036518e48.png)
Autocratic leadership, also known as authoritarian leadership, is a leadership style characterized by individual control over all decisions and little input from group members.
- Autocratic leaders typically make choices based on their ideas and judgments and rarely accept advice from followers. Autocratic leadership involves absolute, authoritarian control over a group.
- Like other leadership styles, the autocratic style has both some benefits and some weaknesses.
- While those who rely on this approach too heavily are often seen as bossy or dictator-like, this level of control can have benefits and be useful in certain situations.