Python Programming - Lab Part B
TIP
This Page supports running Python directly from your browser!
Click for more details. If this feature is not working as expected, please report it to us on Github!
WARNING
This will not work if your browser is too old or does not support Web Assembly/Web Workers. If you're using a privacy focused browser like cromite, please enable JavaScript JIT and WebAssembly from the permissions menu.
If the Run Button doesn't show the run or loading button, try reloading your browser!
It will take some time to load, especially if your internet is slow.
Some examples are run with JupyterLite instead for compatibility with matplotlib and other libraries. The iframe embeds are generated with https://examdawn.github.io/url-py
Program 1: Demonstrate use of Basic Regular Expressions *
python
import re
text = "Hello There!"
#re.match() tries to match a pattern at the beginning of the string.
match = re.match("Hello", text)
print("Match: ", match.group() if match else None)
# re.search() searches the string for a match, and returns a Match object if there is a match.
search = re.search("BCA", text)
print("Search: ", search.group() if search else None)
#re.findall() returns a list containing all matches.
findall = re.findall("[0-9]", text)
print("Findall: ", findall)
# re.split() returns a list where the string has been split at each match.
split = re.split(r"\s", text)
print("Split: ", split)
#re.sub() replaces the matches with the text of choice.
sub = re.sub("4th", "Third", text)
print("Sub: ", sub)Show Output
Match: Hello
Search: None
Findall: []
Split: ['Hello', 'There!']
Sub: Hello There!Try it out
python
import re
text = "Hello There!"
#re.match() tries to match a pattern at the beginning of the string.
match = re.match("Hello", text)
print("Match: ", match.group() if match else None)
# re.search() searches the string for a match, and returns a Match object if there is a match.
search = re.search("BCA", text)
print("Search: ", search.group() if search else None)
#re.findall() returns a list containing all matches.
findall = re.findall("[0-9]", text)
print("Findall: ", findall)
# re.split() returns a list where the string has been split at each match.
split = re.split("\s", text)
print("Split: ", split)
#re.sub() replaces the matches with the text of choice.
sub = re.sub("4th", "Third", text)
print("Sub: ", sub)Program 2: Demonstrate use of Advanced Regular Expressions for Data Validation
python
import re
def validate_data():
email = input("Enter Email Addr: ")
phone = input("Enter Mobile Number: ")
url = input("Enter a URL: ")
password = input("Enter Password: ")
email_regex = r'\S+@\S+\.\S+'
phone_regex = r'\d{10}'
url_regex = r'https?://(www\.)?(\S+\.\S+)'
password_regex = r'.{8,}'
if not re.fullmatch(email_regex, email):
print("Invalid Email Address")
elif not re.fullmatch(phone_regex, phone):
print("Invalid Phone")
elif not re.fullmatch(url_regex, url):
print("Invalid URL")
elif not re.fullmatch(password_regex, password):
print("Invalid Password. Minimum 8 Characters.")
else:
print("Data is Valid.")
validate_data()Show Output
Enter Email Addr: example@email.net
Enter Mobile Number: 1234567890
Enter a URL: https://example.net
Enter Password: password123
Data is Valid.Try it out
python
import re
def validate_data():
email = input("Enter Email Addr: ")
phone = input("Enter Mobile Number: ")
url = input("Enter a URL: ")
password = input("Enter Password: ")
email_regex = r'\S+@\S+\.\S+'
phone_regex = r'\d{10}'
url_regex = r'https?://(www\.)?(\S+\.\S+)'
password_regex = r'.{8,}'
if not re.fullmatch(email_regex, email):
print("Invalid Email Address")
elif not re.fullmatch(phone_regex, phone):
print("Invalid Phone")
elif not re.fullmatch(url_regex, url):
print("Invalid URL")
elif not re.fullmatch(password_regex, password):
print("Invalid Password. Minimum 8 Characters.")
else:
print("Data is Valid.")
validate_data()Program 3: Demonstrate use of List *
python
my_list = [10, 20, 30, 3.142, 'Python', 'BCA']
print("Initial List: ", my_list)
print("Element at list index 0: ", my_list[0])
print("Element at list index 2: ", my_list[2])
my_list[4] = 'Java'
print("List after modifying an item: ", my_list)
my_list.append('ExamDawn')
print("List after appending an item: ", my_list)
my_list.remove('Java')
print("List after removing an item: ", my_list)
del my_list[0]
print("List after deleting an item: ", my_list)
print("Popped item: ", my_list.pop(1))
print("List after popping an item: ", my_list)
print("Index of 'BCA': ", my_list.index('BCA'))
print("Count of '3.142'", my_list.count(3.142))
print("Length of List: ", len(my_list))
my_list.reverse()
print("Reversed List: ", my_list)
my_list.clear()
print("List after clearing: ", my_list)Show Output
Initial List: [10, 20, 30, 3.142, 'Python', 'BCA']
Element at list index 0: 10
Element at list index 2: 30
List after modifying an item: [10, 20, 30, 3.142, 'Java', 'BCA']
List after appending an item: [10, 20, 30, 3.142, 'Java', 'BCA', 'ExamDawn']
List after removing an item: [10, 20, 30, 3.142, 'BCA', 'ExamDawn']
List after deleting an item: [20, 30, 3.142, 'BCA', 'ExamDawn']
Popped item: 30
List after popping an item: [20, 3.142, 'BCA', 'ExamDawn']
Index of 'BCA': 2
Count of '3.142' 1
Length of List: 4
Reversed List: ['ExamDawn', 'BCA', 3.142, 20]
List after clearing: []Try it out
python
my_list = [10, 20, 30, 3.142, 'Python', 'BCA']
print("Initial List: ", my_list)
print("Element at list index 0: ", my_list[0])
print("Element at list index 2: ", my_list[2])
my_list[4] = 'Java'
print("List after modifying an item: ", my_list)
my_list.append('ExamDawn')
print("List after appending an item: ", my_list)
my_list.remove('Java')
print("List after removing an item: ", my_list)
del my_list[0]
print("List after deleting an item: ", my_list)
print("Popped item: ", my_list.pop(1))
print("List after popping an item: ", my_list)
print("Index of 'BCA': ", my_list.index('BCA'))
print("Count of '3.142'", my_list.count(3.142))
print("Length of List: ", len(my_list))
my_list.reverse()
print("Reversed List: ", my_list)
my_list.clear()
print("List after clearing: ", my_list)Program 4: Demonstrate use of Dictionaries *
python
my_dict = {'name': 'Souhrud', 'age': 19, 'city': 'Bangalore'}
print("Initial dictionary:", my_dict)
print("Value for 'name':", my_dict['name'])
print("Value for 'age':", my_dict['age'])
print("Value for 'country':", my_dict.get('country'))
print("Value for 'country' with default:", my_dict.get('country', 'India'))
my_dict['age'] = 25
print("Dictionary after modifying an item:", my_dict)
my_dict['job'] = 'Developer'
print("Dictionary after adding an item:", my_dict)
del my_dict['city']
print("Dictionary after deleting an item by key:", my_dict)
print("Popped item:", my_dict.pop('job'))
print("Dictionary after popping an item:", my_dict)
print("Keys:", list(my_dict.keys()))
print("Values:", list(my_dict.values()))
print("Items:", list(my_dict.items()))
print("Number of items:", len(my_dict))
print("'name' in dictionary:", 'name' in my_dict)
print("'city' in dictionary:", 'city' in my_dict)
my_dict2 = {'country': 'India', 'job': 'Developer'}
my_dict.update(my_dict2)
print("Dictionary after merging:", my_dict)
my_dict.clear()
print("Dictionary after clearing:", my_dict)Show Output
Initial dictionary: {'name': 'Souhrud', 'age': 19, 'city': 'Bangalore'}
Value for 'name': Souhrud
Value for 'age': 19
Value for 'country': None
Value for 'country' with default: India
Dictionary after modifying an item: {'name': 'Souhrud', 'age': 25, 'city': 'Bangalore'}
Dictionary after adding an item: {'name': 'Souhrud', 'age': 25, 'city': 'Bangalore', 'job': 'Developer'}
Dictionary after deleting an item by key: {'name': 'Souhrud', 'age': 25, 'job': 'Developer'}
Popped item: Developer
Dictionary after popping an item: {'name': 'Souhrud', 'age': 25}
Keys: ['name', 'age']
Values: ['Souhrud', 25]
Items: [('name', 'Souhrud'), ('age', 25)]
Number of items: 2
'name' in dictionary: True
'city' in dictionary: False
Dictionary after merging: {'name': 'Souhrud', 'age': 25, 'country': 'India', 'job': 'Developer'}
Dictionary after clearing: {}Try it out
python
my_dict = {'name': 'Souhrud', 'age': 19, 'city': 'Bangalore'}
print("Initial dictionary:", my_dict)
print("Value for 'name':", my_dict['name'])
print("Value for 'age':", my_dict['age'])
print("Value for 'country':", my_dict.get('country'))
print("Value for 'country' with default:", my_dict.get('country', 'India'))
my_dict['age'] = 25
print("Dictionary after modifying an item:", my_dict)
my_dict['job'] = 'Developer'
print("Dictionary after adding an item:", my_dict)
del my_dict['city']
print("Dictionary after deleting an item by key:", my_dict)
print("Popped item:", my_dict.pop('job'))
print("Dictionary after popping an item:", my_dict)
print("Keys:", list(my_dict.keys()))
print("Values:", list(my_dict.values()))
print("Items:", list(my_dict.items()))
print("Number of items:", len(my_dict))
print("'name' in dictionary:", 'name' in my_dict)
print("'city' in dictionary:", 'city' in my_dict)
my_dict2 = {'country': 'India', 'job': 'Developer'}
my_dict.update(my_dict2)
print("Dictionary after merging:", my_dict)
my_dict.clear()
print("Dictionary after clearing:", my_dict)Program 5: Create SQLite Database and Perform Operations on tables *
python
import sqlite3
def display_rows(cursor):
rows = cursor.fetchall()
for row in rows:
print(row)
conn = sqlite3.connect('employee.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS emp")
cursor.execute("""
CREATE TABLE emp
(empno INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
empname TEXT,
salary REAL,
department TEXT)""")
print("Table Created")
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO emp VALUES (1 , 'Souhrud' , 50000 , 'IT')")
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO emp VALUES (2 , 'John' , 35000 , 'Sales')")
conn.commit()
print("Records inserted")
cursor.execute("SELECT * from emp")
print("Records in the table:")
display_rows(cursor)
cursor.execute("UPDATE emp SET salary = 100000 WHERE empno = 1")
conn.commit()
print("Record Updated")
cursor.execute("SELECT * from emp")
print("Records in the table after update:")
display_rows(cursor)
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE emp")
conn.commit()
print("Table Dropped")
conn.close()Try it out
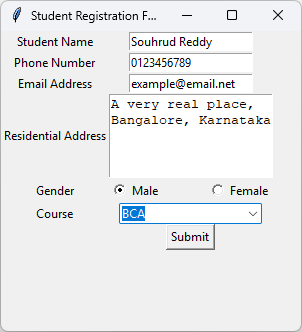
Program 6: Create GUI using Tkinter Module
python
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox, ttk
def submit():
messagebox.showinfo("Submitted", "Form Submitted Successfully.")
root = tk.Tk()
root.geometry("300x300")
root.title("Student Registration Form")
tk.Label(root, text="Student Name").grid(row=0)
tk.Label(root, text="Phone Number").grid(row=1)
tk.Label(root, text="Email Address").grid(row=2)
tk.Label(root, text="Residential Address").grid(row=3)
tk.Label(root, text="Gender").grid(row=4)
tk.Label(root, text="Course").grid(row=5)
name_entry = tk.Entry(root)
phone_entry = tk.Entry(root)
email_entry = tk.Entry(root)
address_text = tk.Text(root, width=20, height=5)
name_entry.grid(row=0, column=1)
phone_entry.grid(row=1, column=1)
email_entry.grid(row=2, column=1)
address_text.grid(row=3, column=1)
gender_var = tk.StringVar()
tk.Radiobutton(root, text="Male", variable=gender_var, value="Male").grid(row=4,column=1, sticky='w')
tk.Radiobutton(root, text="Female", variable=gender_var, value="Female").grid(row=4,column=1, sticky='e')
course_var = tk.StringVar()
course_combobox = ttk.Combobox(root, textvariable=course_var)
course_combobox['values'] = ('BCA','BBA','BCOM')
course_combobox.grid(row=5, column=1)
tk.Button(root, text="Submit", command=submit).grid(row=10,column=1)
root.mainloop()Show Output
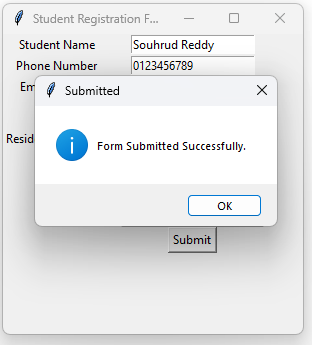
Program 7: Demonstrate exceptions in Python *
python
try:
num = int(input("Enter a number: "))
except ValueError:
print("That's not a valid number!")
else:
print(f"You entered {num}.")
finally:
print("This statement is always executed.")Show Output
Enter a number: 5
You entered 5.
This statement is always executed.Try it out
python
try:
num = int(input("Enter a number: "))
except ValueError:
print("That's not a valid number!")
else:
print(f"You entered {num}.")
finally:
print("This statement is always executed.")Program 8: Drawing Line Chart and Bar Chart using Matplotlib *
Line Chart
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [1,2,3,4,5]
y = [1,4,9,16,25]
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.title("Simple Line Graph")
plt.xlabel("Number")
plt.ylabel("Square")
plt.show()
plt.savefig("simple_line_graph.png")Try it out
Bar Chart
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
courses = ["BCA","BCOM", "BBA", "BSc", "BA" ]
count = [120, 180, 60, 30, 80]
plt.bar(courses, count, color="maroon", width=0.4)
plt.xlabel("Courses")
plt.ylabel("Count")
plt.title("Count of Students in Different Courses")
plt.show()Try it out
Program 9: Drawing Histograms and Pie Chart using Matplotlib *
Histogram
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ages = [25, 22, 23, 23, 30, 31, 22, 35, 34, 56, 27, 45, 41, 19, 19, 26, 32, 33, 45, 40]
plt.hist(ages, bins=5, edgecolor='black')
plt.title('Ages of Customers')
plt.xlabel('Age')
plt.ylabel('Number')
plt.show()Try it out
Pie Chart
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Data
languages = ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
votes = [250, 150, 100, 75, 50]
# Create a pie chart
plt.figure(figsize=[5,5])
plt.pie(votes, labels=languages, autopct='%1.1f%%')
plt.title('Favorite Programming Languages')
plt.show()Try it out
Program 10: Create array using Numpy and Perform Operations on Array
python
import numpy as np
#Create two arrays
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
#Perform arithmetic operations
print("Addition:", a + b)
print("Subtraction:", a - b)
print("Multiplication:", a * b)
print("Division:", a / b)
#Perform relational operations
print("a Greater than b", a > b)
print("a Less than b", a < b)
print("a Equal to b:", a == b)
print("a Not Equal to b:", a != b)
#Perform logical operations
print("Logical OR:", np.logical_or(a, b))
print("Logical AND:", np.logical_and(a, b))
print("Logical NOT:", np.logical_not(a))
#Perform aggregation functions
print("Sum of a:", np.sum(a))
print("Max of b:", np.max(b))
print("Min of a:", np.min(a))
print("Average of b:", np.average(b))
# Perform matrix operations
print("Matrix Addition:\n", a + b)
print("Matrix Subtraction:\n", a - b)
print("Matrix Multiplication (element-wise):\n", a* b)
print("Matrix Multiplication:\n", np.matmul(a, b))
print("Transpose of a:\n", np.transpose(a))
#Perform statistical functions
print("Standard Deviation:", np.std(a))
print("Variance:", np.var(a))
print("Median:", np.median(a))
#Reshape array
c = a.reshape((3, 1))
print("Reshaped a:", c)
#Stack arrays
print("Horizontal Stack:\n", np.hstack((a, b)))
print("Vertical Stack:\n", np.vstack((a, b)))
#Split array
d= np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8]])
print("Horizontal Split:\n", np.hsplit(d, 2))
print("Vertical Split:\n", np.vsplit(d, 2))
#Broadcasting
print("Broadcasting addition:\n", a + 5)Try it out
Program 11: Create Data Frame from Excel Sheets using Pandas and Perform Operations on Data Frames
python
import pandas as pd
#Read DataFrame from excel file
df = pd.read_excel("emp.xlsx")
#Data selection of single column print("Single column: \n", df[ 'Name'])
#Data selection of double columns
print("\nDouble columns: \n", df[['Name', 'Gender']])
# Select first row by index label using .loc[]
print("\nFirst row using loc[]:\n", df.loc[0])
# Select first row by position using iloc[] print("\nFirst row using .iloc[]: \n", df.iloc[0])
#Slice the first two rows and select 'Student Name' and 'Age' columns print("The first two rows of Name and Age Columns: ")
print(df[:2][['Name', 'Age']])
#Filtering based on age>30
print("\nFiltered DataFrame (Age > 30):\n", df[df['Age'] > 30])
# Grouping based on Course and Age
grouped_df = df.groupby('Gender') ['Age'].mean()
print("\nGrouped DataFrame (based on 'Gender' and 'Age'):\n", grouped_df)
# Sorting by index
df_by_index= df.sort_index(ascending=False)
print("\nDataFrame sorted by index: \n", df_by_index)
# Sorting by values
df_by_value = df.sort_values (by='Age')
print("\nDataFrame sorted by 'Age' column: \n", df_by_value)Sample Data: https://showai.undo.it/sample_data/emp.xlsx
Show Output
Double columns:
Name Gender
0 Alice Female
1 Bob Male
2 Charlie Male
3 Daisy Female
First row using loc[]:
Name Alice
Gender Female
Age 28
Department HR
Name: 0, dtype: object
Name Age
0 Alice 28
1 Bob 35
Filtered DataFrame (Age > 30):
Name Gender Age Department
1 Bob Male 35 IT
2 Charlie Male 40 Finance
Grouped DataFrame (based on 'Gender' and 'Age'):
Gender
Female 26.5
Male 37.5
Name: Age, dtype: float64
DataFrame sorted by index:
Name Gender Age Department
3 Daisy Female 25 Marketing
2 Charlie Male 40 Finance
1 Bob Male 35 IT
0 Alice Female 28 HR
DataFrame sorted by 'Age' column:
Name Gender Age Department
3 Daisy Female 25 Marketing
0 Alice Female 28 HR
1 Bob Male 35 IT
2 Charlie Male 40 Finance